Resolving server failover issues
Important: You need 'sudo' permissions to upgrade software or make changes to configuration files. If you do not have this access, contact your organization's systems administrator.
Currently, Redhat and Rocky 8 Linux installs are affected by a standard network configuration issue where the bonding mode value is interrupting a server failover. If the BONDING_OPTS bonding mode is 802.ad and the miimon is set to default 0, link monitoring is disabled and the bonding driver is not able to trigger a failover. If you are experiencing a link failure, your network configuration may be affected by this issue. Check the network configuration settings on the server to determine if the server is affected.
If you're having this issue, there are two options to fix the issue. Both require maintenance on the server, so be sure to notify the appropriate teams in your organization before making the change.
You can change the BONDING_OPTS line in your network configuration file. We recommend this option.
If you have kernel software installed on your server, upgrading the software to the latest version can resolve the issue.
Bonding mode 802.3ad is a link aggregation mode that uses the LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) network protocol to negotiate between the bond adapter and the switch within a network. LACP combines multiple network interfaces into a single interface enabling them to act as a single interface to support the total bandwidth. Essentially, if one link in the aggragate group fails, the traffic is redistributed to the remaining active links.
This protocol uses the miimon (Media Independent Interface Monitor) parameter to monitor the link status of the bonded interface specifying the frequency (in milliseconds) in which the bonding driver checks the status of each interface. (For example, setting miimon=100 means the driver will check the link status every 100 milliseconds.)
If a link failure is detected, the bonding driver triggers a failover to another active interface, ensuring network redundancy and high availability for the traffic. If the miimon value is set to 0, the link driver does not check the link status of the interfaces, assuming they are always up.
Option 1: Change the miimon value (recommended)
You can change the miimon value in the network configuration file to resolve the server failover issue. Use the following steps to determine if the network configuration has the BONDING_OPTS miimon set to 0 and how to make the necessary changes to fix the issue. Follow your organization's procedures for making changes to configuration files.
To change the miimon value:
Note: Notify your operational teams before you begin any maintenance and again after it is complete.
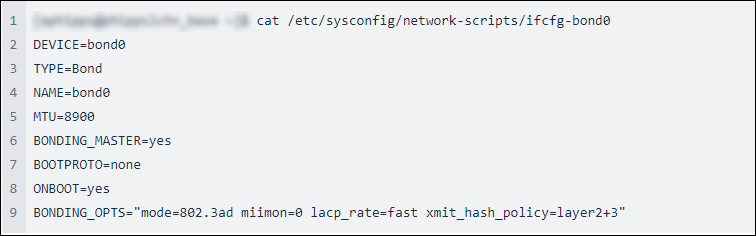
- Check your network configuration to determine if it is affected by typing the following command in your command line prompt.
When you run the command, the system shows the network configuration details. If the BONDING_OPTS mode is 802.3ad and the miimon is set to 0, the configuration is affected by the failover issue. Continue with the steps to fix the issue.
- Make a backup copy of the ifcfg-bond0 configuration file before you make any changes.
- Edit the ifcfg-bond0 file.
- Remove the BONDING_OPTS line that has the miimon value set to 0.
- Add the BONDING_OPTS line that has the miimon value set to 100 by typing or copying the following:
- Save the file and exit.
- Isolate the traffic from the SASE (secure access service edge) or affected server to prepare the server to be rebooted.
- Wait until all traffic is off the server, then shut down server applications.
- Reboot the server.
- Wait for the server to come back up completely, log in, then verify connectivity.
- Check that all applications have resumed running. If not, start them manually.
- Route the traffic back to the server.
- Repeat the same steps (1‑12) on the failover or backup server.
Option 2: Upgrade the kernel version
You can upgrade the kernel version on your server to resolve the server failover issue. The current version of kernel has the miimon default value set to 100. Follow your organization's procedures for performing updates. Upgrade to the current version by entering these commands in your command line prompt.
To upgrade the kernel version:
Note: Notify your operational teams before you begin any maintenance and again after it is complete.
- Check the version of kernel on your server.
- Update the package list to make sure it is current before upgrading your version of kernel.
- Upgrade to the most current version of kernel.
- Reboot your system to apply the new kernel upgrade.
- Verify the new version of kernel is running.




